Roselle – 5 Seeds
(Hibiscus sabdariffa)
R30.00
The Roselle plant has many culinary and medicinal uses. It is an ideal crop to grow in your garden.
Common Names: Roselle, Jamaica sorrel, red sorrel (En); oseille de Guinée, karkadé, bissap, groseille pays (Fr); rosa de Jamaica and sereni (Sp).
Indoor Sowing: Late Winter and Early Spring.
Direct Sowing: Spring and Summer.
Out of stock
Email me when the product is back in stock.
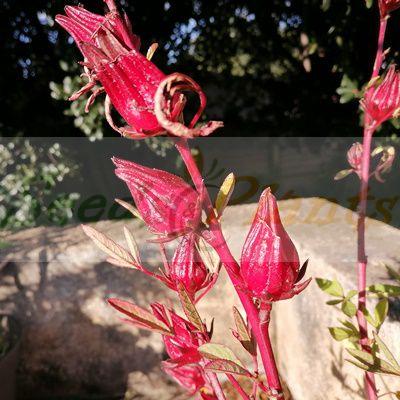
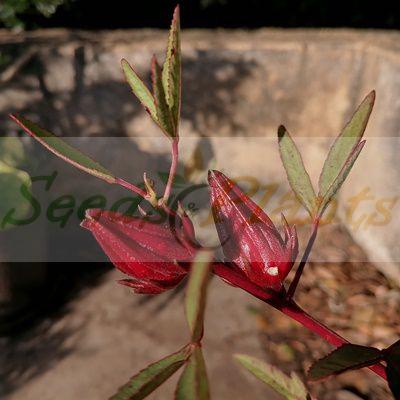
Roselle Seeds. Hibiscus sabdariffa, also known as Roselle, is an ideal crop as it is relatively easy to grow. In China the seeds are used for their oil and the plant is used for its medicinal properties, while in West Africa the leaves and powdered seeds are used in meals. Additionally, it is used in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
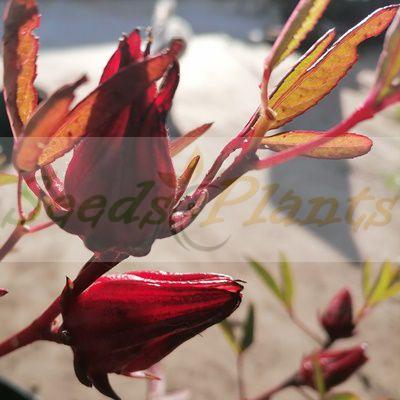
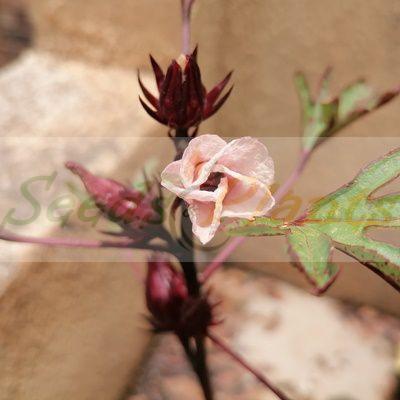
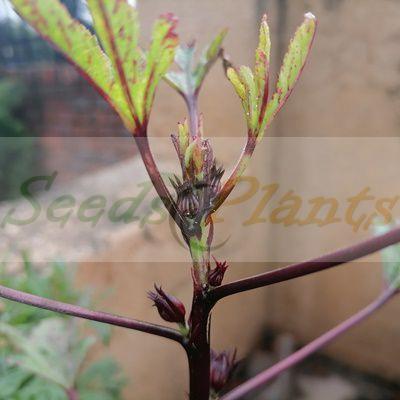
It is an annual or perennial herb or woody-based subshrub, growing to 2–2.5 m tall. The flowers are 8–10 cm in diameter, white to pale yellow with a dark red spot at the base of each petal, and have a stout fleshy calyx at the base, 1–2 cm wide, enlarging to 3–3.5 cm, fleshy and bright red as the fruit matures. They take about six months to mature.
The species is hermaphrodite (has both male and female organs) and is pollinated by Insects.
Roselle Culinary Uses
- The fresh calyx is eaten raw in salads, is cooked and used as a flavoring in cakes.
- It is also used in making jellies, soups, sauces, pickles, puddings.
- The calyx is rich in citric acid and pectin and is useful for making jams, jellies.
- It is also used to add a red color and to flavor to herbal teas and can be roasted and used as a coffee substitute.
- Tender young leaves and stems can be eaten raw or cooked.
- Used in salads, as a potherb and as a seasoning in curries, they have an acid, rhubarb-like.
- The seeds can be roasted and ground into a powder then used in oily soups and sauces.
- The roasted seeds have been used as a coffee substitute that is said to have aphrodisiac properties.
Roselle Medicinal Uses
- Roselle is an aromatic, astringent, cooling herb that is much used in the Tropics.
- It is said to have diuretic effects, to help lower fevers and is antiscorbutic.
- The leaves are antiscorbutic, emollient, diuretic, refrigerant, and sedative.
- The leaves are very mucilaginous and are used as an emollient and as a soothing cough remedy.
- They are used externally as a poultice on abscesses.
- The fruits are antiscorbutic.
- The flowers contain gossypetin, anthocyanin, and the glycoside hibiscin. These may have diuretic and choleretic effects, decreasing the viscosity of the blood, reducing blood pressure and stimulating intestinal peristalsis.
- The leaves and flowers are used internally as a tonic tea for digestive and kidney functions.
- Experimentally, an infusion decreases the viscosity of the blood, reduces blood pressure and stimulates intestinal peristalsis.
- The ripe calyces are diuretic and antiscorbutic.
- The succulent calyx, boiled in water, is used as a drink in the treatment of bilious attacks.
- The seeds are diuretic, laxative and tonic. They are used in the treatment of debility.
- The bitter root is aperitif and tonic.
- The plant is also reported to be antiseptic, aphrodisiac, astringent, cholagogue, demulcent, digestive, purgative and resolvent.
- It is used as a folk remedy in the treatment of abscesses, bilious conditions, cancer, cough, debility, dyspepsia, dysuria, fever, hangover, heart ailments, hypertension, neurosis, scurvy, and strangury.
Growing Roselle
Indoor Sowing: Late Winter and Early Spring.
Direct Sowing: Spring and Summer.
- To grow hibiscus from seed you must first scarify the seed by nicking or sanding the seeds. This helps to get moisture into the seeds to improve the germination rate.
- Plant the seeds in the growing medium and keep the soil moist until germination.
- In temperate zones, start hibiscus in pots at the same time as you would tomatoes.
- When seedlings are about 11cm, transplant them to a sunny spot in the garden.
- Hibiscus grows well in soil with a high level of organic matter, but too much nitrogen will delay flowering.
- Keep plants evenly moist & well-weeded until they are about 60cm high.
- Once this height is reached, mulch the plants to retain moisture and keep weeds at bay.
- Suitable for: light (sandy), medium (loamy) and heavy (clay) soils and prefers well-drained soil.
- Suitable pH: acid, neutral and basic (alkaline) soils.
- It cannot grow in the shade. It prefers moist soil.
Harvesting Roselle
Pick young calyxes by hand when still tender or use garden clippers once stems have gotten tough. Pick approx. 10 days after flowers open at the beginning or the end of the day. Harvesting the calyxes early promotes greater yields. Around 6 weeks, the young edible leaves & shoots can be picked.
Fresh calyxes are typically dried or dehydrated prior to storage. You can keep them fresh in the ‘fridge for 4 – 7 days. Leaves & stem tips can be stored in the refrigerator for about a week.
Disclaimer
Medicinal Information:
All medicinal information on this website is for educational and informational purposes only and may not be construed as medical advice. The information is not intended to replace medical advice or treatment offered by healthcare professionals.
Seeds, Plants, Plant Cuttings, Geophytes and Dried Herbs:
In some countries and provinces, certain plants are deemed as invasive and are not allowed to be planted at all, whilst some plants are allowed to be grown only in certain areas or provinces. The onus is on you as the buyer to familiarize yourself with the regulations pertaining to your location, before purchasing any of our seeds, plants, plant cuttings, geophytes or dried herbs. We will not be held liable, should you purchase any seeds, plants, plant cuttings, geophytes or dried herbs. from us which are prohibited in your country or province.