Licorice Vine – 5 Seeds
(Abrus precatorius)
R50.00
Licorice Vine seeds are valued in making necklaces for their bright coloration and the leaves and root of the plant is used medicinally.
Common Names: Crab’s eye, rosary pea, paternoster pea, love pea, precatory pea or bean, prayer bead, John Crow Bead, coral bead, red-bead vine, country licorice, Indian licorice, wild licorice, Jamaica wild licorice, Akar Saga, coondrimany, gidee gidee, Jumbie bead, ratti/rettee/retty, amabope (Ndebele), nsimani (Shangaan), and umkhokha (Zulu) and weather plant.
Indoor Sowing: Late Winter.
Direct Sowing: Late Winter and Early Spring.
Only 3 left in stock
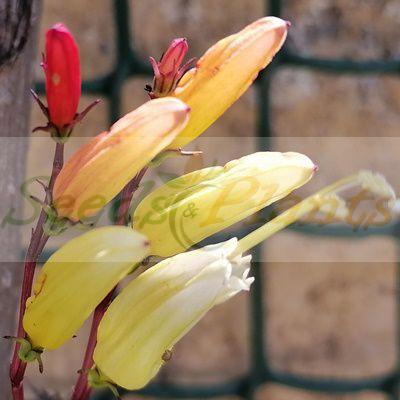
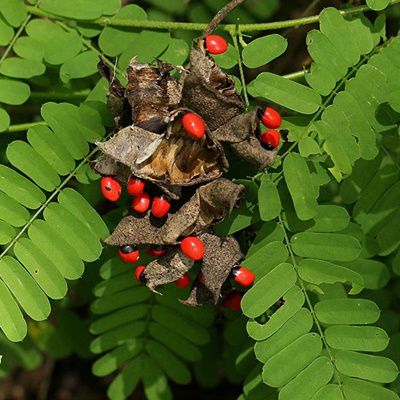
Licorice vine (Abrus precatorius) is a perennial flowering plant in the bean family Fabaceae. It is a slender, perennial climber that twines around trees, shrubs, and hedges. Flowers are small and pale violet with a short stalk, arranged in clusters. The shiny red and black seeds of Abrus precatorius make it a sought-after climber in tropical and subtropical areas. In South Africa, it is distributed in KwaZulu-Natal, Mpumalanga and some parts of Limpopo. Its leaves are consumed as a vegetable in central and east Africa.
Common names include: Crab’s eye, rosary pea, paternoster pea, love pea, precatory pea or bean, prayer bead, John Crow Bead, coral bead, red-bead vine, country licorice, Indian licorice, wild licorice, Jamaica wild licorice, Akar Saga, coondrimany, gidee gidee, Jumbie bead, ratti/rettee/retty, amabope (Ndebele), nsimani (Shangaan), and umkhokha (Zulu) or weather plant.
WARNING: The seeds of this plant are very poisonous and can be dangerous to humans and animals if consumed. Ingesting just 1 seed can kill a person! The plant secretes a toxin called abrin which is closely related to ricin. The symptoms of these toxins are severe stomach pains, diarrhea, nausea, cold sweats, drowsiness, colic, and weak and fast pulse.
Licorice vine Medicinal and other Uses
- Traditionally the seeds were used for decorative and gold-weighing purposes.
- The seeds are valued in making necklaces for their bright coloration.
- The plant is also used externally in some traditional medicine to treat mainly scratches and sores, and wounds caused by dogs, cats and mice.
- The leaves and roots of this plant are used in South Africa to treat tuberculosis, bronchitis, whooping cough, chest complaints, and asthma.
- The leaves of the plants also are used as tea by Tanzanian traditional healers to treat epilepsy.
Growing Licorice vine
Indoor Sowing: Late Winter.
Direct Sowing: Late Winter and Early Spring.
- It is adaptable to most soils, but prefers a tropical climate with reasonably high rainfall and a sunny position.
- Because the plant can become invasive, it is advisable to grow it in containers.
- To enhance germination, scarify the seed and then soak the seeds overnight in very hot water.
- Sow the seeds immediately afterwards in seeding mix and cover with a layer of soil.
- Germination takes about 30 days or longer with pre-treatment and erratically without.
Disclaimer
Medicinal Information:
All medicinal information on this website is for educational and informational purposes only and may not be construed as medical advice. The information is not intended to replace medical advice or treatment offered by healthcare professionals.
Seeds, Plants, Plant Cuttings, Geophytes and Dried Herbs:
In some countries and provinces, certain plants are deemed as invasive and are not allowed to be planted at all, whilst some plants are allowed to be grown only in certain areas or provinces. The onus is on you as the buyer to familiarize yourself with the regulations pertaining to your location, before purchasing any of our seeds, plants, plant cuttings, geophytes or dried herbs. We will not be held liable, should you purchase any seeds, plants, plant cuttings, geophytes or dried herbs. from us which are prohibited in your country or province.